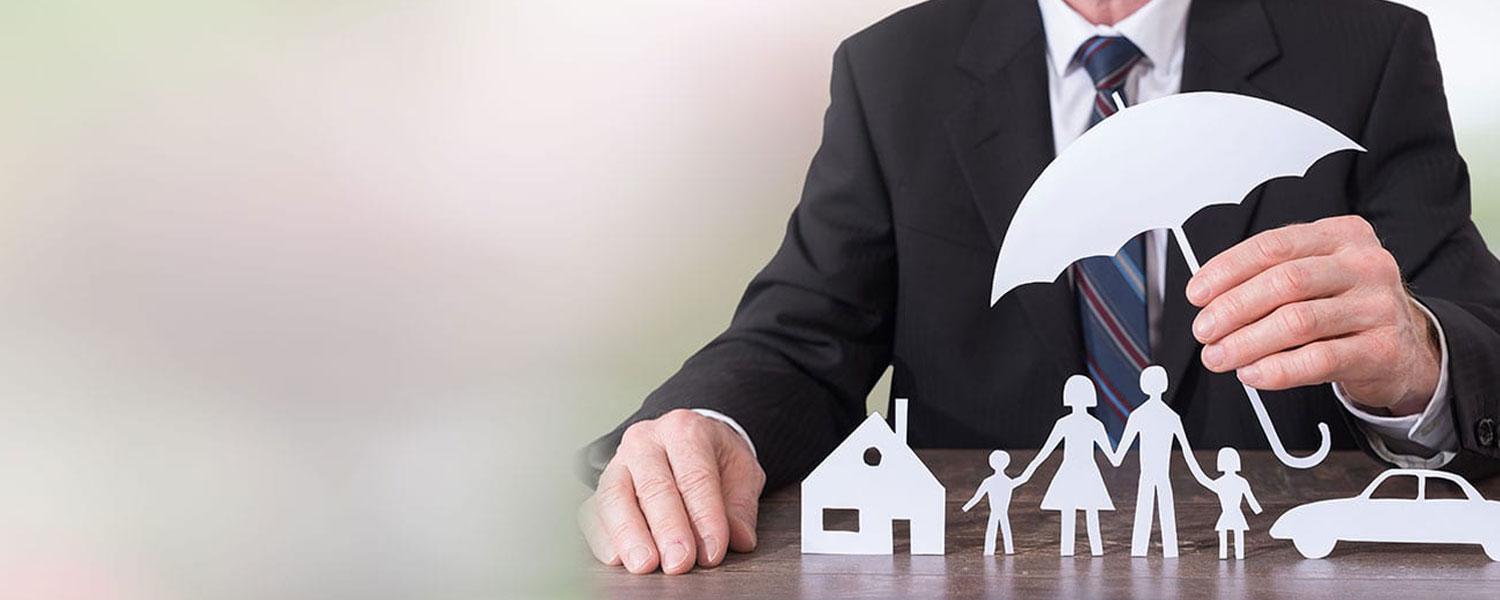
A general insurance policy is a contract between an
individual or entity (the policyholder) and an insurance company, providing
financial protection against specific risks other than life. Here’s a detailed
overview of general insurance policies:
Key Components of a
General Insurance Policy
1. Policyholder and Insurer:
Policyholder: The individual or entity
purchasing the insurance.
Insurer: The insurance company providing the
coverage.
2. Coverage Details:
Insured Assets: The specific items or interests covered
(e.g., property, vehicle, health).
Risks Covered: Specific risks or perils covered
by the policy (e.g., fire, theft, accidents, health issues).
Exclusions: Specific risks or conditions not
covered by the policy (e.g., pre-existing conditions in health insurance, wear
and tear in property insurance).
3. Policy Term:
The duration for which the policy is valid,
usually one year, after which it must be renewed.
4. Premium:
The amount paid by the policyholder to the
insurer to maintain the coverage. Premiums can be paid annually, semi-annually,
quarterly, or monthly.
5. Sum Insured:
The maximum amount the insurer will pay for a
covered loss.
6. Deductibles and Co-pays:
Deductible: The amount the policyholder must pay
out-of-pocket before the insurer pays a claim.
Co-pay: A percentage of the claim amount that
the policyholder must pay.
7. Policy Documents:
The official documents outlining the terms,
conditions, coverage, exclusions, and endorsements of the insurance policy.
Types of General
Insurance Policies
1. Health Insurance:
Covers medical expenses, hospitalization,
surgeries, and preventive care. Policies can include individual plans, family
floater plans, and critical illness plans.
2. Motor Insurance:
Third-Party Liability: Covers damages to third
parties caused by the insured vehicle.
Comprehensive Coverage: Covers third-party
liability and damages to the insured vehicle due to accidents, theft, fire, and
natural disasters.
3. Home Insurance:
Covers damages to the home and its contents due
to fire, theft, natural disasters, and other specified risks.
4. Travel Insurance:
Covers trip cancellations, medical emergencies,
lost luggage, and other travel-related incidents.
5. Property Insurance:
Protects commercial and personal properties
against risks like fire, theft, and natural disasters.
6. Liability Insurance:
Covers legal liabilities to third parties for
damages or injuries. This includes public liability, product liability, and
professional liability insurance.
7. Marine Insurance:
Covers goods, cargo, ships, and other maritime
interests against losses or damages during transit.
Claims Process
Filing a Claim: The policyholder must notify the
insurer of a loss or damage, providing necessary documentation and evidence.
Assessment: The insurer assesses the claim,
verifying the validity and extent of the loss.
Approval and Payment: Once approved, the insurer
pays the claim amount according to the policy terms, less any deductibles or
co-pays.